Author: James Organ | Posted On: 08 Aug 2025
Updates to this research are published monthly.
Labour market conditions remain weak
Hiring intent remains in very negative territory for the next three months. This reflects the broader softness in the labour market, as evidenced by the rise in the seasonally adjusted unemployment rate to 4.3% in June. The proportion of SMEs with current job vacancies also dropped sharply from 15% in June to 10% in July, the lowest level in over a year, suggesting further upward pressure on unemployment.
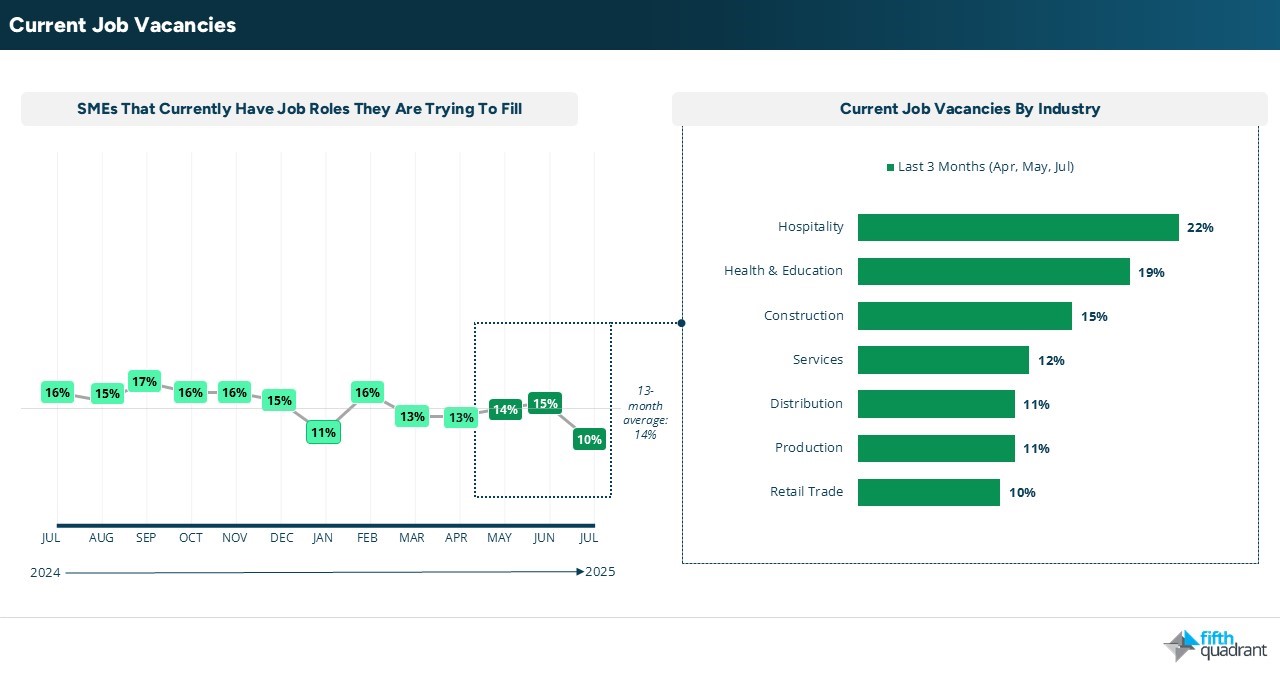
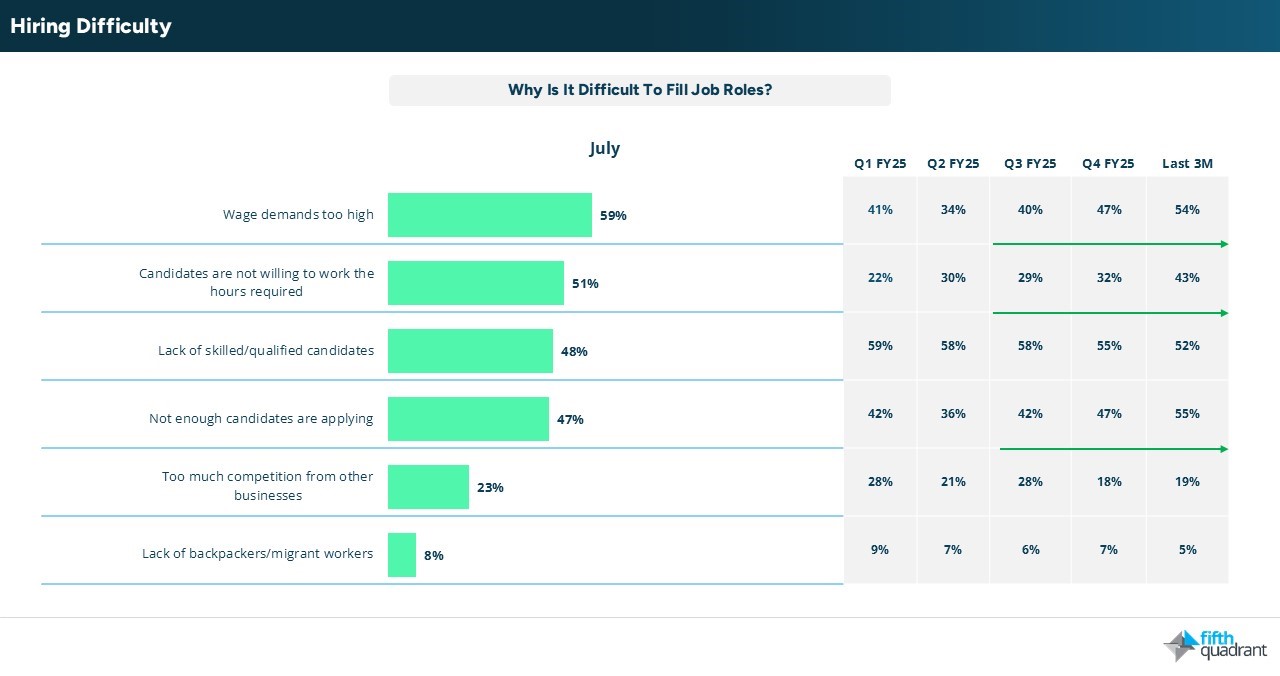
Vacancy levels among smaller SMEs (0 to 19 employees) fell to 7% in July, marking the lowest level this year, while vacancy activity among larger SMEs remains volatile amid broader economic uncertainty. Among those still hiring, businesses are reporting higher wage demands, reduced willingness among candidates to work required hours, and a limited pool of applicants. This may reflect not only hiring challenges but also a decline in workforce participation, as some individuals step away from the job market entirely.
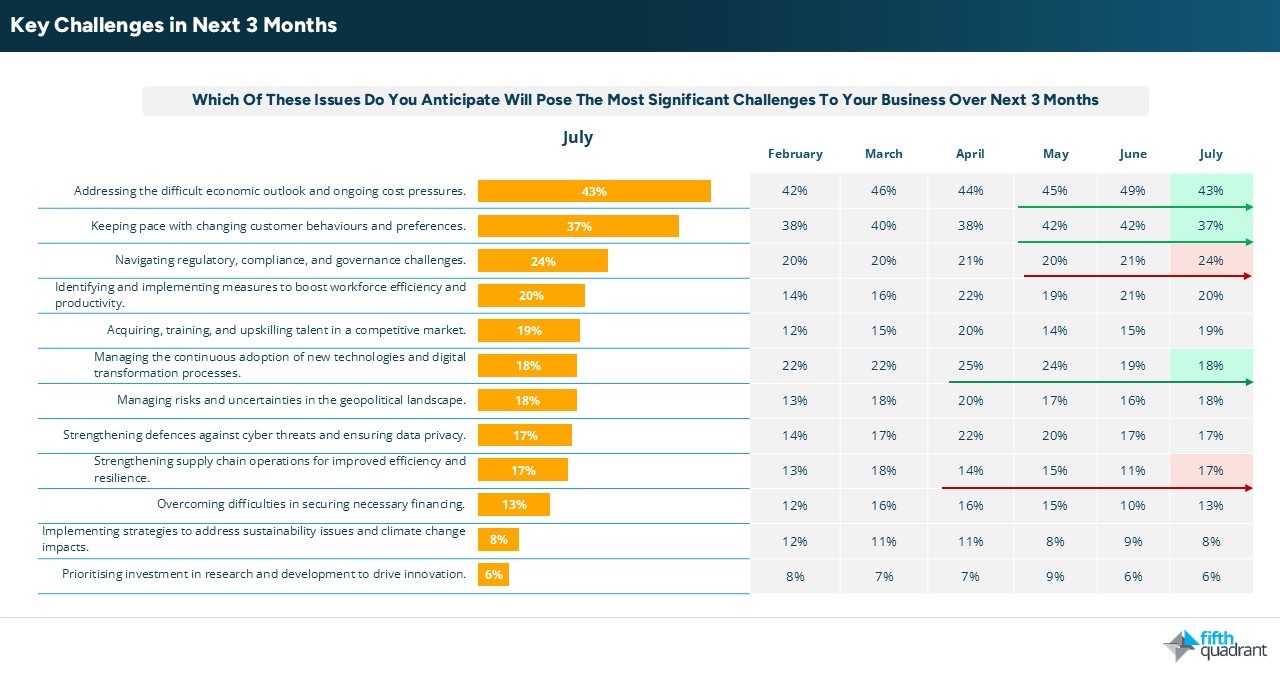
Cost pressures and operational challenges persist
SMEs continue to rank cost pressures as their most significant challenge, followed by changing customer behaviours and regulatory demands. While some challenges have softened, others, such as regulatory compliance and supply chain efficiency have increased. These shifts are likely driven by persistent tariff-related issues.
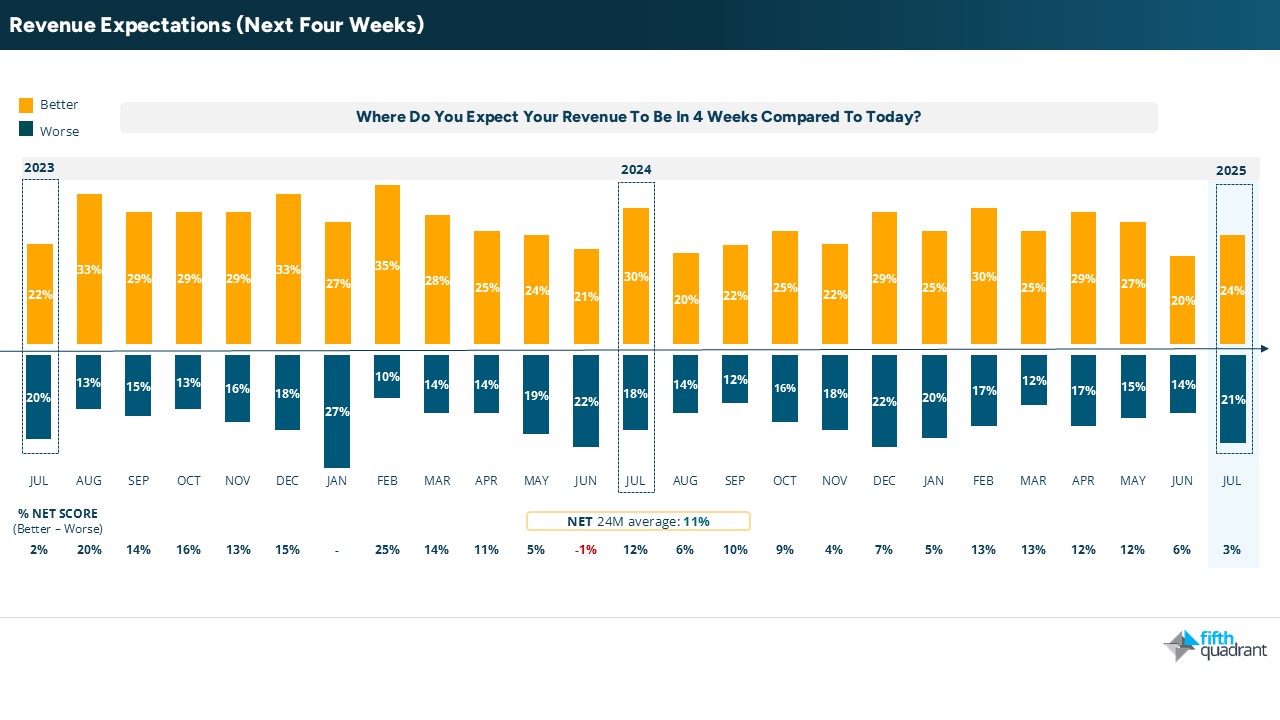
Mixed signals on business growth and investment
Despite weak confidence in both domestic and global economies, growth expectations rebounded to 35% in July, recovering from June’s dip. This suggests SMEs are entering FY2026 with renewed ambition. However, this optimism is not yet reflected in short-term trading indicators, with revenue expectations for the next four weeks falling to a NET 3%, the lowest since June 2024.
Similarly, capital expenditure and marketing spend intentions declined in July, contradicting the stated growth ambitions. That said, larger SMEs showed a positive rebound in capex intentions following a weak end to FY2025, hinting at selective investment confidence among more established businesses.
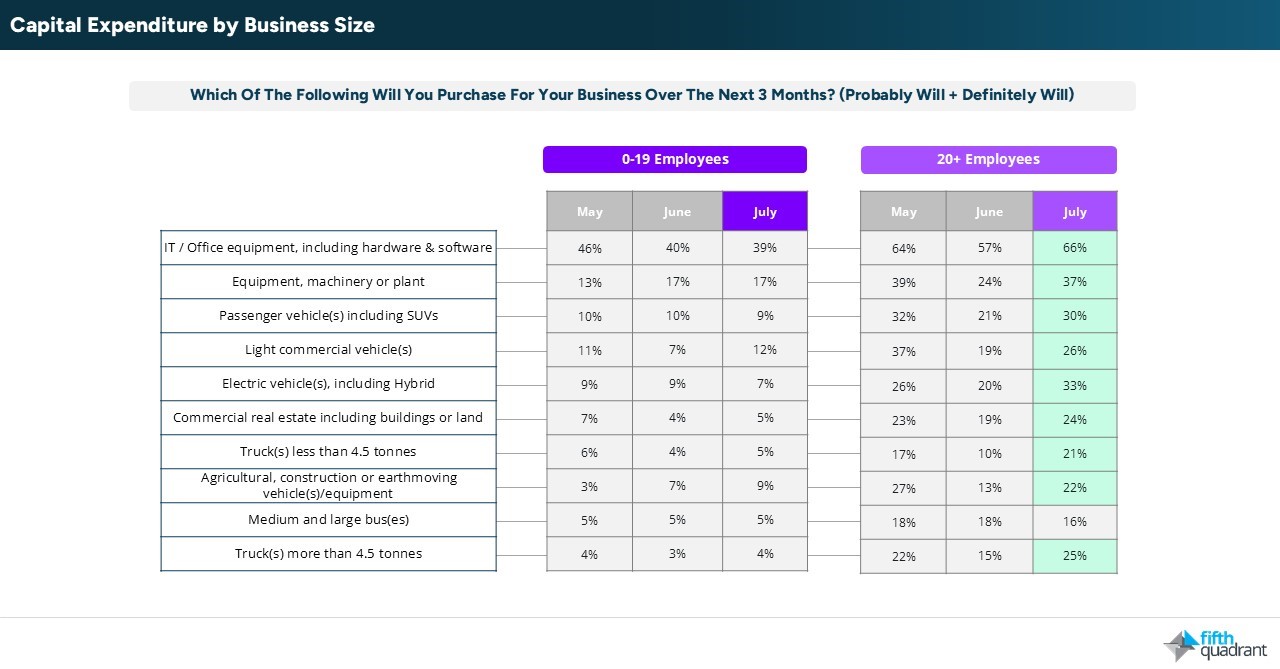
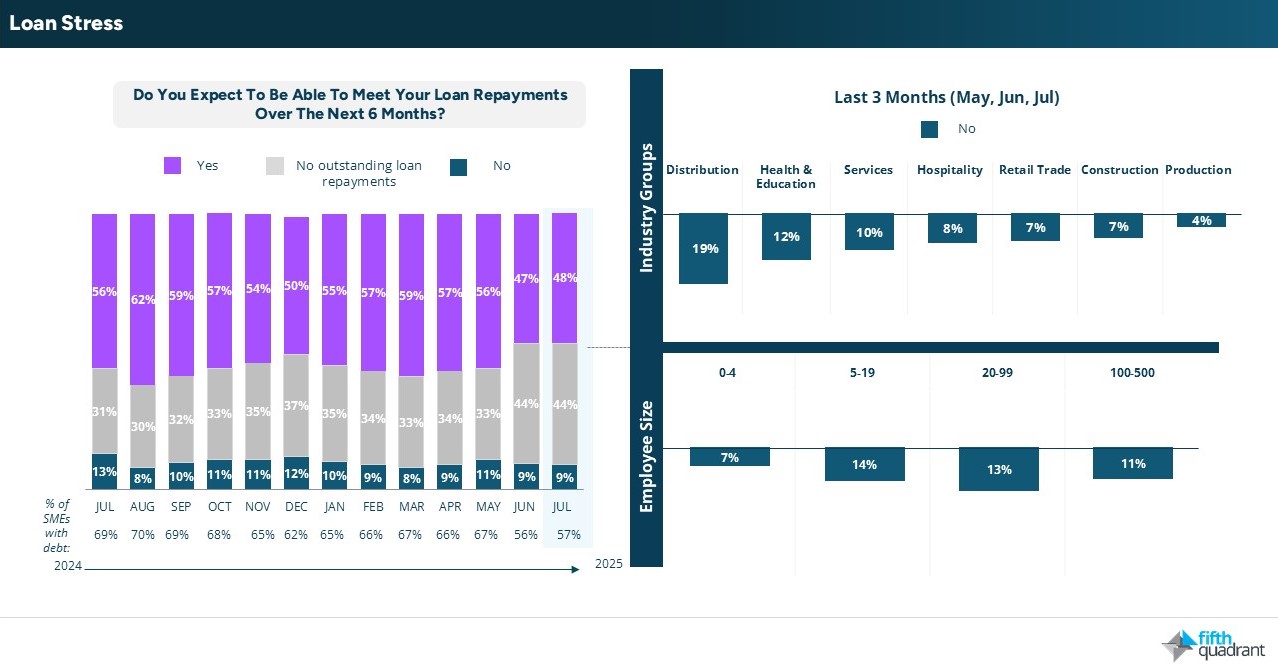
Finance demand and loan stress trends
Demand for finance softened across most sectors, with only Distribution, Hospitality, and Retail showing an increase. This underlines the need for additional working capital in consumer-facing sectors that are under pressure. Meanwhile, loan stress remained steady, with 9% of SMEs unsure whether they will be able to meet their repayment obligations over the next six months.
Conclusion
Rising unemployment, falling vacancy rates, and softening investment signal a bumpy start to FY2026. While SMEs remain ambitious about growth, subdued revenue expectations and persistent cost pressures suggest those plans may prove difficult to deliver. Conditions are expected to remain challenging over the next six months, particularly for consumer-facing sectors under financial strain.
Please click the link below to access the full report including subgroup analysis by industry sector, size of business and state. Fifth Quadrant and Ovation Research publish monthly updates of this SME market research here. For any questions or inquiries, feel free to contact us here.

SMEs remain resilient
Posted in B2B, Consumer & Retail, Financial Services

